
DNA extraction
To begin working with DNA we have to first isolate it. The first isolation of DNA was done in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher. [7] Currently it is a routine procedure in molecular biology or forensic analyses. For the chemical method, there are many different kits used for extraction, and selecting the correct one will save time on kit optimization and extraction procedures.
Basic procedure
- Cells which are to be studied need to be collected.
- Breaking the cell membranes open to expose the DNA along with the cytoplasm within (cell lysis).
- Lipids from the cell membrane and the nucleus are broken down with detergents and surfactants.
- Breaking down proteins by adding a protease (optional).
- Breaking down RNA by adding an ribonuclease (optional).
- The solution is treated with a concentrated salt solution (saline) to make debris such as broken proteins, lipids and RNA clump together.
- Centrifugation of the solution, which separates the clumped cellular debris from the DNA.
- DNA purification from detergents, proteins, salts and reagents used during the cell lysis step using various organic solvents (ethanol, isopropanol, phenol chloroform etc.). [7]
Types of extraction
Organic extraction involves the addition of and incubation in multiple different chemical solutions [7a], including a lysis step, a phenol chloroform extraction, an ethanol precipitation, and washing steps. Organic extraction is often used in laboratories because it is cheap, and it yields large quantities of pure DNA.
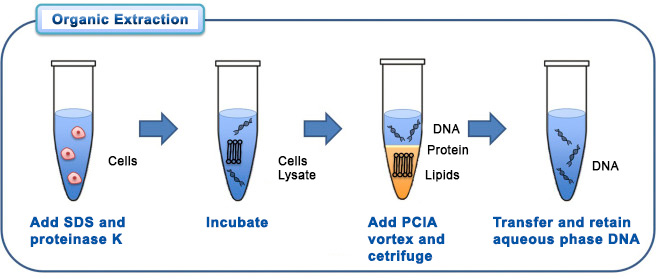
Legend: SDS - sodium dodecylsulfate; Proteinase K - enzyme; PCIA - phenol-chloroform isoamyl alcohol; [9]
Chelex extraction method involves adding the Chelex resin to the sample, boiling the solution, then vortexing and centrifuging it. The cellular materials bind to the Chelex beads, while the DNA is available in the supernatant (upper leyer of solution acfter centrifugating). [7b] The Chelex method is much faster and simpler than organic extraction, and it only requires one tube, which decreases the risk of DNA contamination but it yealds much lower quantity of DNA.
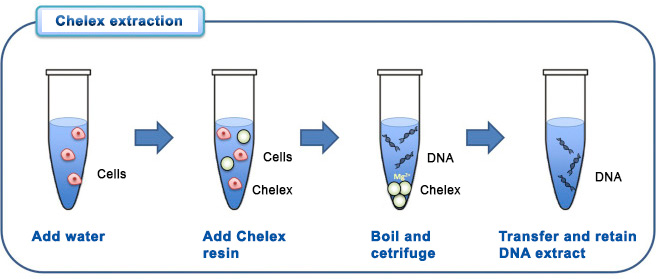
Legend: Chelex resin - ions exchange resin in organic chemistry; [9]
Solid phase extraction such as using a spin-column based extraction method takes advantage of the fact that DNA binds to silica gel. The sample containing DNA is added to a column containing a silica gel or silica beads and chaotropic salts. The chaotropic salts disrupt the hydrogen bonding between strands and facilitate binding of the DNA to silica by causing the nucleic acids to become hydrophobic. This exposes the phosphate residues so they are available for adsorption. [7c] The DNA binds to the silica, while the rest of the solution is washed out using ethanol to remove chaotropic salts and other unnecessary constituents. [7d] The DNA can then be rehydrated with aqueous low salt solutions allowing for elution of the DNA from the beads.
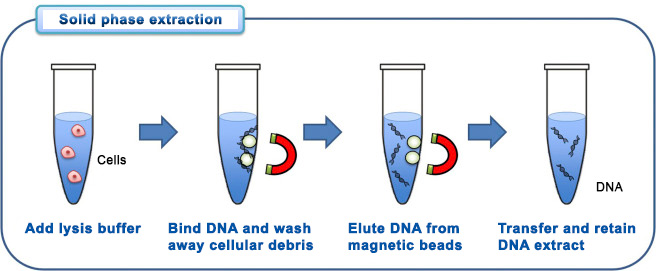
Legend: Lysis buffer - chemical buffer; [9]
© www.humankaryotype.com